Docker
Table of contents
General
Docker is an open-source software platform for creating, deploying, and managing virtualized application containers. With Docker, applications and their environment can be provided in parallel and isolated on a host system.
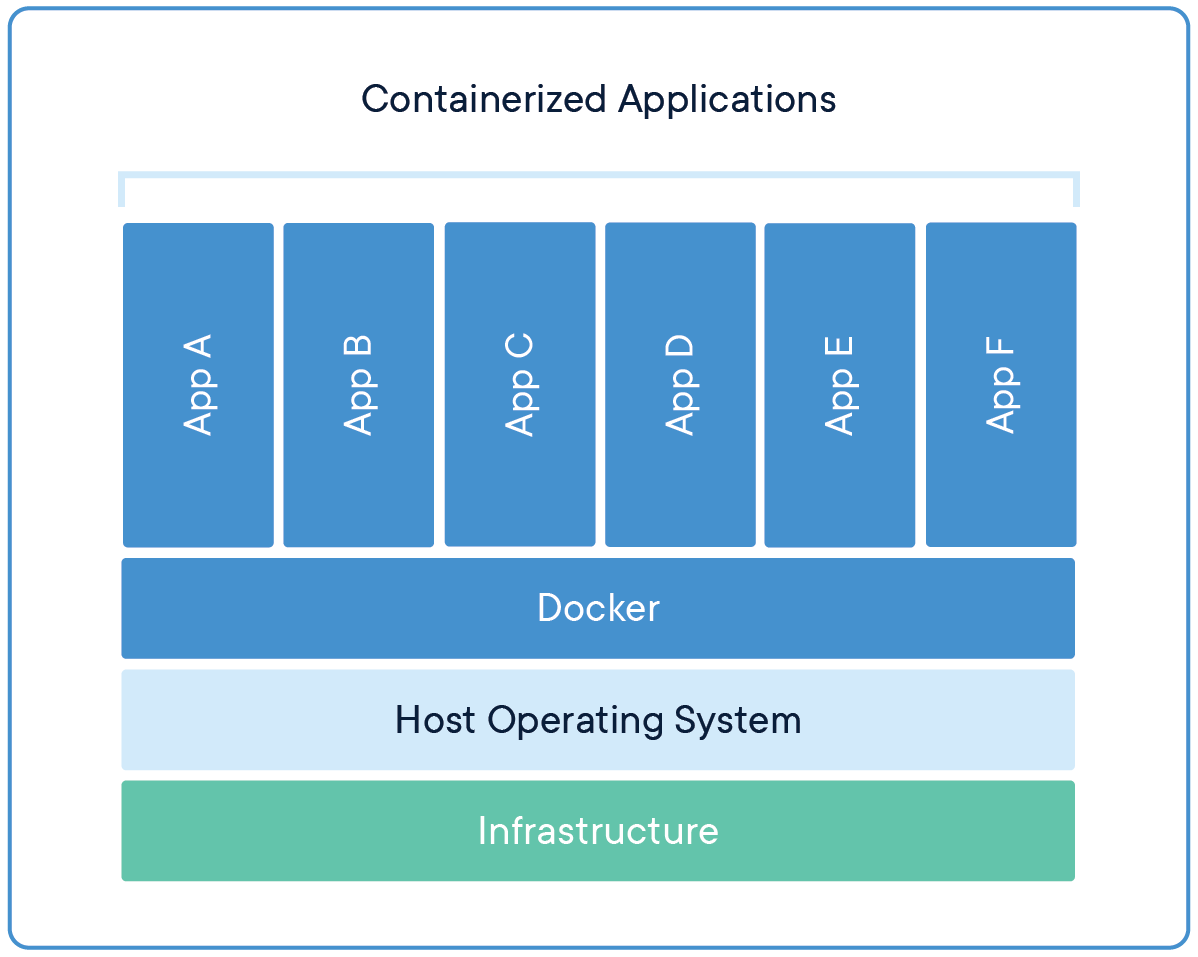
A container is a lightweight virtual software that packages the application source code with all its dependencies, such as system libraries (libs), binary files, external packages, etc.
Some benefits of using docker are:
- Easy to move and maintain the applications;
- Easy to scale due to fast deployment and ability to quickly create new instances;
- A “cleaner environment” enables less software dependency.
Some drawbacks are:
- The performance may reduce when compared to the non-docker/virtual machine alternative due to limited resources;
- Data cannot be persisted inside a container;
- Monitoring ability is not so good.
Docker image
Each container is based on a docker image, which is similar to an OS Installation Disk, but allows infinite customization. Images are typically built from a Dockerfile, which is a plaintext file that specifies all of the components that are included in the container.
Images can be stored on public Docker repositories, such as Docker Hub, or private repositories, such as the Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR). Amazon ECR also has a public repository, Amazon ECR Public Gallery.
Virtual Machines vs Containers
Virtual Machines are an abstraction that allows a single server to be turned into multiple serves thanks to the hypervisor. Each VM includes a full copy of the OS and consumes a fixed amount of RAM, Disk, and CPU that was allocated to it before the VM was initialized. Some advantages of VMs are that they are more secure than containers and they have the ability to persist data.
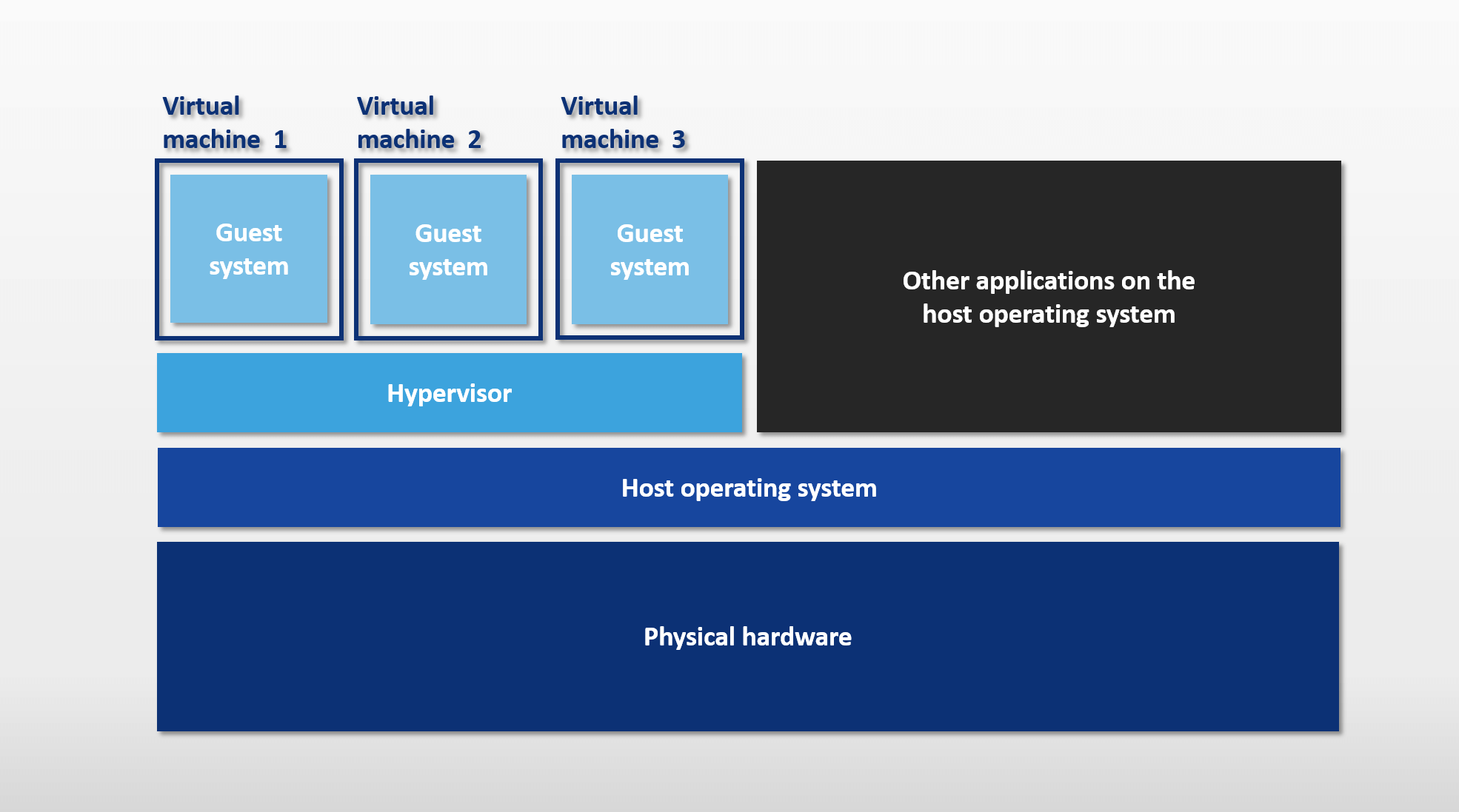
Containers, on the other hand, utilize the same OS as the Host, which means Containers are smaller than VMs. Additionally, containers do not require compute and storage allocation, which ensures all the compute power is available for the containers and the Host.